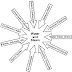
The waste water source of Coal Runoff WWT is from Coal yard sedimentation pond. The process block diagram is as follow :
figure 1. simplified coal runoff block diagram
1. Coagulation
2. Floculation
3. Clarification or Sedimentation
4. Filtration
5. Neutralization
6. Sludge thickening
Coagulation is destabilization process of suspended solid colloid material with coagulant agent to produce micro floc using rapid-mix.
Floculation is floc formation process which basically uses agglomeration grouping between particles and coagulants with gentle mixing to combine several particles into large floc.
Sedimentation is the process by which suspended solid particle are removed from the water by means of gravity or separation. Sedimentation involves one or more basins, called Clarifier. In properly designed clarifier, the velocity of the water is reduced so that gravity is the predominant force acting on the water/solid suspension. The key factor in this process is speed. The rate at which a floc particle drops out of the water has to be faster than the rate at which the water flows from the tank's inlet or slow mix end to its outlet or filtration end. The difference in specific gravity between the water and the particles causes the particles to settle to the bottom of the basin. Some plants have added baffles or weirs in the sedimentation basins to limit short-circulating through the basin, promoting better settling.
To maximize the sedimentation rate, usually used Lamella Clarifier. Inclined tubes and plates can be used in sedimentation basins to allow greater loading rate of sedimentation. This technology relies on the theory of reduced-depth sedimentation : particles need only settle to the surface of the tube or plate below for removal from the process flow. Generally, a space of two inches is provided between tube walls or plates to maximize settling efficiency. The typical angle of inclination is about 60 degrees, so that settled solid slide down to the bottom of the basin.
figure 2. lamella clarifier
Filtration is a process used to separate solids from liquids or gases using a filter medium that allows the fluid to pass through but not the solid. The term "filtration" applies whether the filter is mechanical, biological, or physical. The fluid that passes through the filter is called the filtrate. The filter medium may be a surface filter, which is a solid that traps solid particles, or a depth filter, which is a bed of material that traps the solid. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as blinding. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective pore size of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles (depending on the pore size, filter thickness and biological activity).
Neutralization is a chemical reaction in which acid and base react to form salt and water. Hydrogen (H+) ions and hydroxide (OH- ions) reacts with each other to form water. The strong acid and strong base neutralization have the pH value of 7. Before discharging the waste water, adjast pH is very important. In Indonesia, keep pH around 6.5 - 8.5.
figure 3. pH scale
The Side process is Heavy Metal Precipitation. This happen at the Coagulation than which injected Precipitation Agent. The principle technology to remove metals pollutants from wastewater is by chemical precipitation. Chemical precipitation includes two secondary removal mechanisms, coprecipitation and adsorption . Precipitation processes are characterized by the solubility of the metal to be removed. They are generally designed to precipitate trace metals to their solubility limits and obtain additional removal by coprecipitation and adsorption during the precipitation reaction. There are many different treatment variables that affect these processes. They include the optimum pH , the type of chemical treatments used, and the number of treatment stages, as well as the temperature and volume of wastewater, and the chemical specifications of the pollutants to be removed. In theory, the precipitation process has two steps, nucleation followed by particle growth. Nucleation is represented by the appearance of very small particle seeds which are generally composed of 10–100 molecules. Particle growth involves the addition of more atoms or molecules into this particle structure. The rate and extent of this process is dependent upon the temperature and chemical characteristics of the wastewater, such as the concentration of metal initially present and other ionic species present, which can compete with or form soluble complexes with the target metal species.
Heavy metals are present in many industrial wastewaters. Examples of such metals are cadmium , copper , lead , mercury , nickel , and zinc. In general, these metals can be complexed to insoluble species by adding sulfide, hydroxide, and carbonate ions to a solution. For example, the precipitation of copper (Cu) hydroxide is accomplished by adjusting the pH of the water to above 8, using precipitant chemicals such as lime (Ca(OH)2) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH). Precipitation of metallic carbonate and sulfide species can be accomplished by the addition of calcium carbonate or sodium sulfide. The removal of coprecipitive metals during precipitation of the soluble metals is aided by the presence of solid ferric oxide, which acts as an adsorbent during the precipitation reaction. For example, hydroxide precipitation of ferric chloride can be used as the source of ferric oxide for coprecipitation and adsorption reactions. Precipitation, coprecipitation, and adsorption reactions generate suspended solids which must be separated from the wastewater. Flocculation and clarification are again employed to assist in solids separation.
figure 4. solubility of various metal vs pH
This Process is in asmuch as the soluble metal is react with a reagent (Sulfide) to form an insoluble metal sulfide complex. The reaction is as below :
Sulfide precipitation is often a more effective alternative to hydroxide since the metal sulfide (MS) generally have lower solubility and much higher binding contants. Thus, the sulfide can displace chelants better than hydroxides and force the reaction toward the insoluble precipitate. Very low levels of metals can be achieved with sulfide precipitation. Copper, cadmium,zink, and mercury can be effectively precipitated with short contact time.
Sulfide precipitation uses either a soluble sulfide or an insoluble sulfide as the source ofbthe sulfide reagent. In soluble sulfide precipitation such as Hydrogen Sulfide ( H2S), Sodium Sulfide ( Na2S), or Sodium Hydrogen Sulfide (NaHS) serve as the source of sulfide. In insoluble sulfide such as Ferrous Sulfide (FeS).









Get the residential water treatment system with us! Aquios® provides an exceptional line of residential salt free water softeners and whole house water filtration systems.
ReplyDeleteAJAY ENTERPRISE is a leading manufacturer and supplier of packaged drinking water plants, water softening plant, Swimming Pool Filter Plant, Domestic & Industrial R.O. Plant, D.M. water plant of all sizes and STP Plant in India. We also serve industries with best installation, maintenance and Industrial water Plant in India, repairing service for water plants of all size and types. AJAY ENTERPRISE was established in 2002 with intent to cater industries with suitable range of water plants. Experience of more than one and half decade has ascertained our position as the prominent mineral water plants distributor.
ReplyDeleteSTP Plant in India
ETP Plant in India
industrial Water Plant in India
Industrial R.O. Plant in Ahmedabad
packaged drinking water in india
water softner in india
D M Water Plant in India
PT TWIN Logistics perusahaan Ppjk ingin mengajukan penawaran kerjasama dalam bidang pengurusan barang Import RESMI & BORONGAN.
ReplyDeleteServices Kami,
Customs Clearance Import sistem Resmi maupun Borongan
Penanganan secara Door to Door ASIA & EROPA Sea & Air Service
Penyediaan Legalitas Under-Name (Penyewaan Bendera Perusahaan)
Pengiriman Domestik antar pulau seluruh Indonesia laut dan Udara atau Darat.
Keterangan tambahan :
1. Nomor Induk Berusaha ( NIB ) : 1257002601078
2. IT ( Mainan, Elektronic, Garmen, Sepatu dan Peralatan kaki lainnya )
3. SPI-PI Besi Baja,
4. SPI-PI Produk Kehutanan,
5. SPI-PI Barang Bekas,
6. SPI-PI Tekstil & Izin TPT
7. Produk-produk Lartas SNI
8. LS ( Laporan Surveyor )
9. LS Alas kaki
10. LS Garment
11. LS Textile
12. LS Electronik
Terima kasih atas kepercayaan kepada kami, semoga kerjasamanya berjalan dengan baik dan lancar.
Jika ada pertanyaan lebih lanjut, Bpk/ Ibu dapat menghubungi Customer Support PT TWIN Logistics melalui Nomor Phone : +62 21 8498-6182, 8591-7811 Whatssapp : 0819-0806-0678 E-Mail : andijm.twinlogistics@yahoo.com
Mr. Andi JM
Hp Whatssapp : 0819-0806-0678 / 0813-8186-4189
= = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = == = = = =
PT TUNGGAL WAHANA INDAH NUSANTARA
Jl. Raya Utan Kayu No.105 B Jakarta Timur 13120 Indonesia
Phone : +62 21 8498-6182, 8591-7811 Fax : +62 21 8591-7812
Email : pt.twinlogistics@yahoo.com, andijm@twin.co.id
Web : www.twinlogistics.co.id , www.twin.co.id